General
|
General Information |
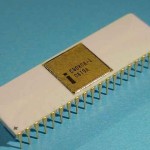
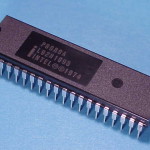
The 8080 was created by the Intel with Federico Faggin as the lead designer (his last chip before he left and started Zilog). The 8080 was released in March of 1974. This chip is date coded to 1976, so it is a very early version of the chip. The 8080 was used in the Altair 8800, the first widely-known personal computer. Because of its increased function and power over the 4004 and 8008, the 8080 was the first widely accepted microprocessor. “The 8080 really created the microprocessor market. The 4004 and 8008 suggested it, but the 8080 made it real.” – Federico Faggin. The 8080 had a 16 bit address bus and an 8 bit data bus. Internally it had seven 8 bit registers (A-E, H, L – pairs BC, DE and HL could be combined as 16 bit registers), a 16 bit stack pointer to memory which replaced the 8 level internal stack of the 8008, and a 16 bit program counter. It also had several I/O ports – 256 of them, so I/O devices could be hooked up without taking away or interfering with the addressing space, and a signal pin that allowed the stack to occupy a separate bank of memory The 8080 family is also referred to as the MCS-80. |
|
Production |
April, 1974 |
| Designers | Federico Faggin, Masatoshi Shima, Stan Mazor |
Architecture
| Type | Data Word | Address Space | Clock | Instruct- ions | Assists | Reg’s GP | Reg’s Math | Reg’s Index | IO Ports | Stack | Interrupts | Memory |
| NMOS,CPU | 8-bit | 64KB | Base 2Mhz, (-2) 2.6Mhz, (-1) 3Mhz | 48 | Ext* | 0 | 1 | 6 8-bit | 512 | Stack Pointer | Vectored, Multi- level | NA |
* Intel made a hardware multiply chip called the 8231 for the 8080
Packages
Modified Packages (I, M, L, and Q)
|
Chip Name |
Package |
On-Chip Identification |
Picture |
General Comments |
| MD8080A/B | Gray Ceramic, 40-pin DIP | MD8080A/B |  |
Military version testing procedure B |
Other 8080 Pictures
 |
|||
| Intel Advertisement for the 8080 |
Related Chips
|
Related Chips |
Intel 8085 |
|
Second Sources |
AMD (8080,AM9080), Mitsubishi (M58710S), NEC (uPD8080A), National Semiconductor (DP8080A), Texas Instruments (TMS8080A) |
| Support Chips | 8205 (Binary Decoder), 8212 (8-bit I/O Port), 8214 (Priority Interrupt Controller), 8216 (4-bit Parallel Bi-directional bus driver), 8224 (Clock generator), 8228 (System controller and bus driver), 8238 (System controller and bus driver (enhanced timing control)), 8251 (Communications Interface), 8253 (Programmable Interval Timer), 8255 (Programmable Peripheral Interface), 8257 (DMA Controller), 8259 (Interrupt Controller), 8271 (Floppy Disk Controller), 8273 (SDLC Protocol Controller), 8275 (CRT Controller), 8279 (Keyboard/Display Interface), 8801 (Clock Crystal for use with the 8224) |